MIT 6.824 Lec3: GFS
1. Distributed Storage System
1.1 Fault Tolerance Storage System is hard to build
- high performance $\Rightarrow$ share data across servers
- many servers $\Rightarrow$ constant failures
- fault tolerance $\Rightarrow$ by replication
- replication $\Rightarrow$ potential inconsistencies
- strong consistency $\Rightarrow$ more interactions between servers $\Rightarrow$ low performance
Struggle between Consistency and Performance.
1.2 Ideal Consistency
Ideal Consistency: Behave as if single system.
Two main challenges: Concurrency and Failures.
Need Protocol to get a balance between Consistency and fault tolerance.
2. GFS
A sucuessful system and became a inspiration to subsequent famous distributed storage systems.
two uncommon features at the time:
- A single Master
- inconsistencies
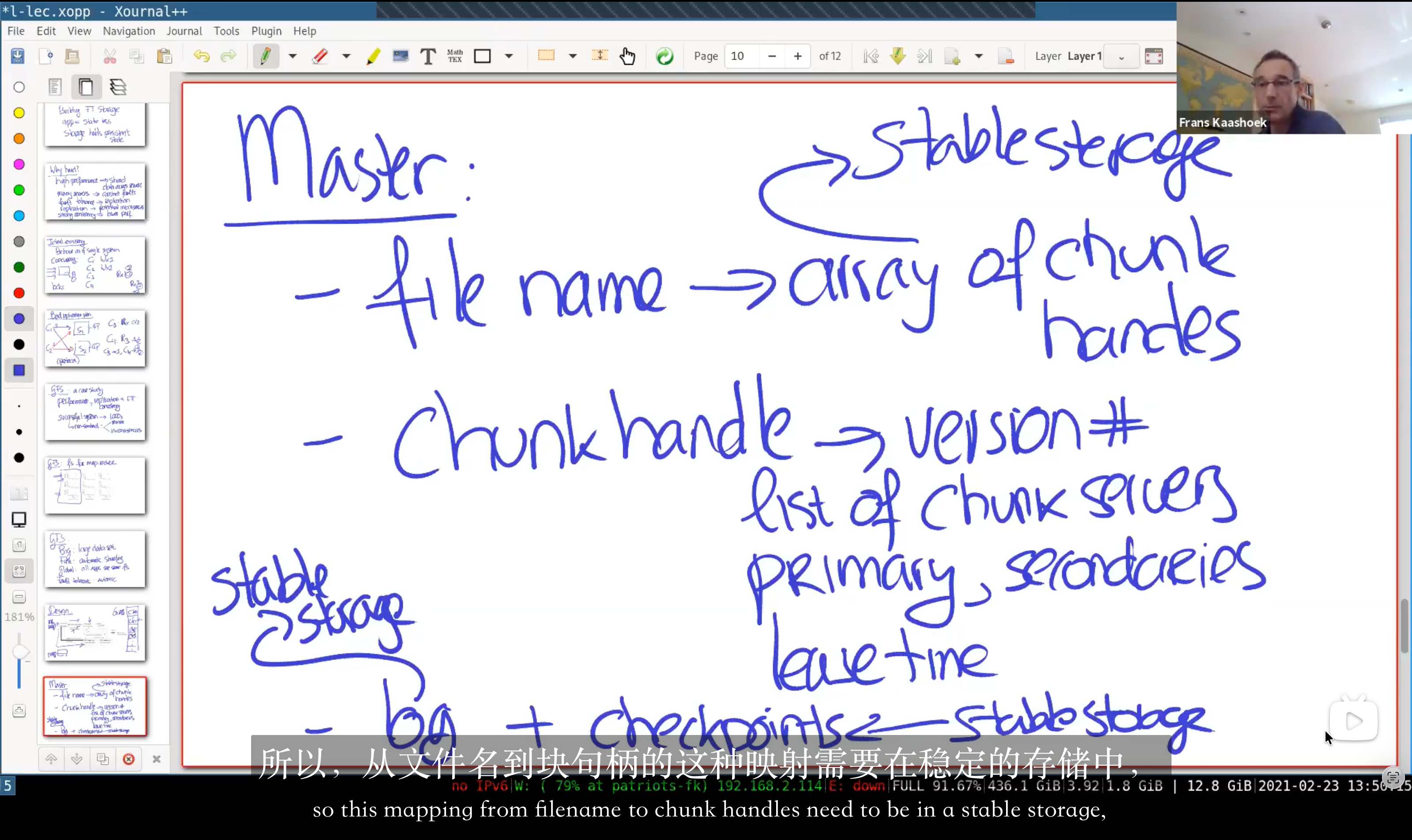
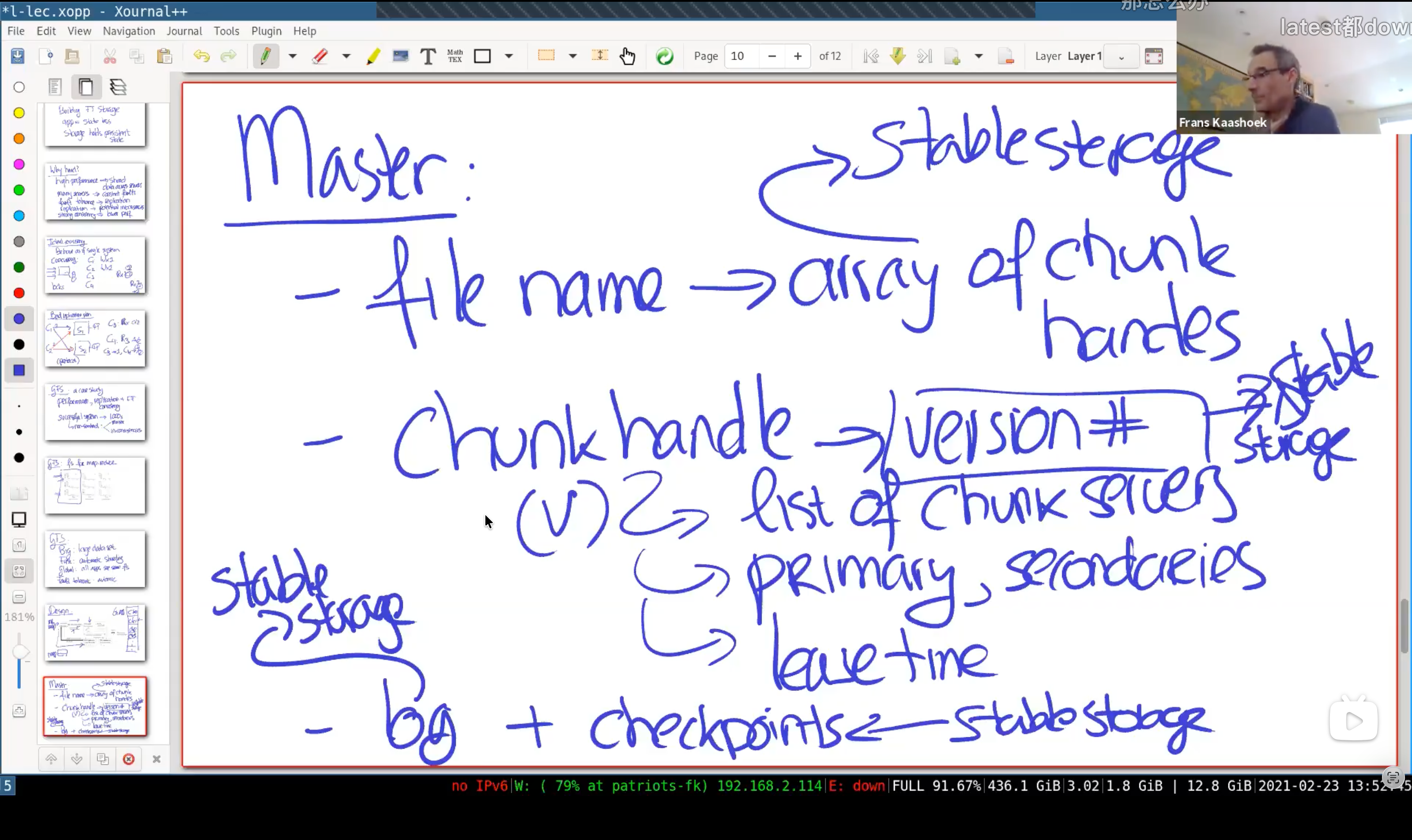
2.1 Master
Master is the crucial control center, it holds (most of them in memory for rapid response to the bunch of clients):
- file name $\rightarrow$ array of chunk handles
- chunk handles $\rightarrow$ version number, list of chunk servers (for replication)
chunk servers: 3 servers in total (including replications), 1 primary, others secondaries.
primary: lease time - log and checkpoints: Both of them are in a stable storage.
GFS follow the rules that we will not response to the cilens before we write our operations record to the log. So when the master carshes, correct states can be reconstructed by replay the log (More precisely, replay all operations in the log after the last checkpoint).
MIT 6.824 Lec3: GFS